Accounting Principles: What They Are and How GAAP and IFRS Work
In 2009, the FASB launched the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC or Codification), which it continues to update. This electronic database contains the official accounting standards (the equivalent of establishing credit terms for customers many thousands of printed pages) which apply to the financial reporting of U.S companies and not-for-profit organizations. The principle of regularity is often cited as the most important GAAP standard.
- For example, if an insurance company receives $12,000 on Dec 28, 2023 to provide insurance protection for the year 2024, the insurance company will report $1,000 of revenue in each of the 12 months in the year 2024.
- Accounting software will permit Joe to generate the financial statements and other reports that he will need for running his business.
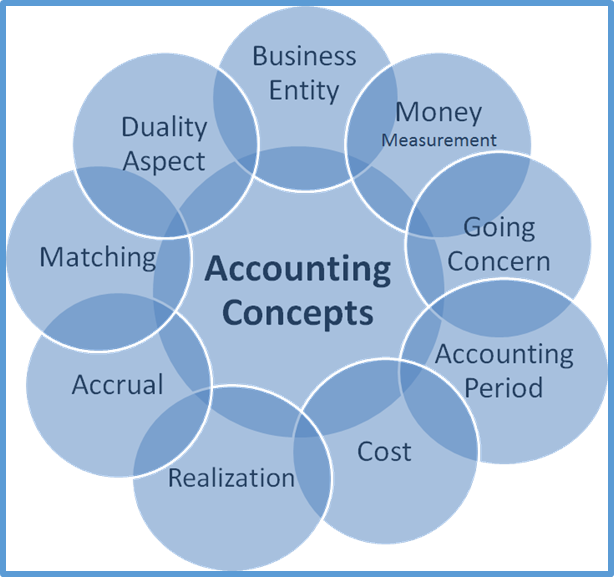
- Introductions to basic accounting often identify assets, liabilities, and capital as the field’s three fundamental concepts.
- Although the value of items and assets changes over time, the gain or loss of your assets is only reflected in their sale or in depreciation entries.
- The monetary unit assumption principle, therefore, is the reasoning behind why you have to go through the extra effort to complete your business bookkeeping for foreign transactions.
Understanding Accounting Principles
An accrual would immediately recognize and record the cost of the contractor’s work, regardless of whether the contractor had actually submitted an invoice or received payment. However, not all business owners have the time or means to pursue formal training. Students sometimes enter accounting programs with little technical knowledge. This guide serves as an easy-to-use resource for developing the vocabulary used by accounting professionals. Professor Roger H. Hermanson, PhD, CPARegents Professor Emeritus of Accounting and Ernst & Young-J.
Table of Contents
Accounting principles are the rules that have emerged from the use of basic accounting concepts. These rules have evolved over a long period of time; they represent the collective wisdom of accounting history. Accounting principles are guidelines to record accurate financial data, help in financial analysis, and maintain transparency.
Relevance and timeliness
An accounting guideline which allows the readers of financial statements to assume that the company will continue on long enough to carry out its objectives and commitments. In other words, the accountants believe that the company will not liquidate in the near future. This assumption also provides some justification for accountants to follow the cost principle. GAAP is a collection of accounting principles and standards that public companies must follow to make sure their financial reporting is consistent. Small businesses can follow suit to maintain good financial hygiene and uniform reporting.
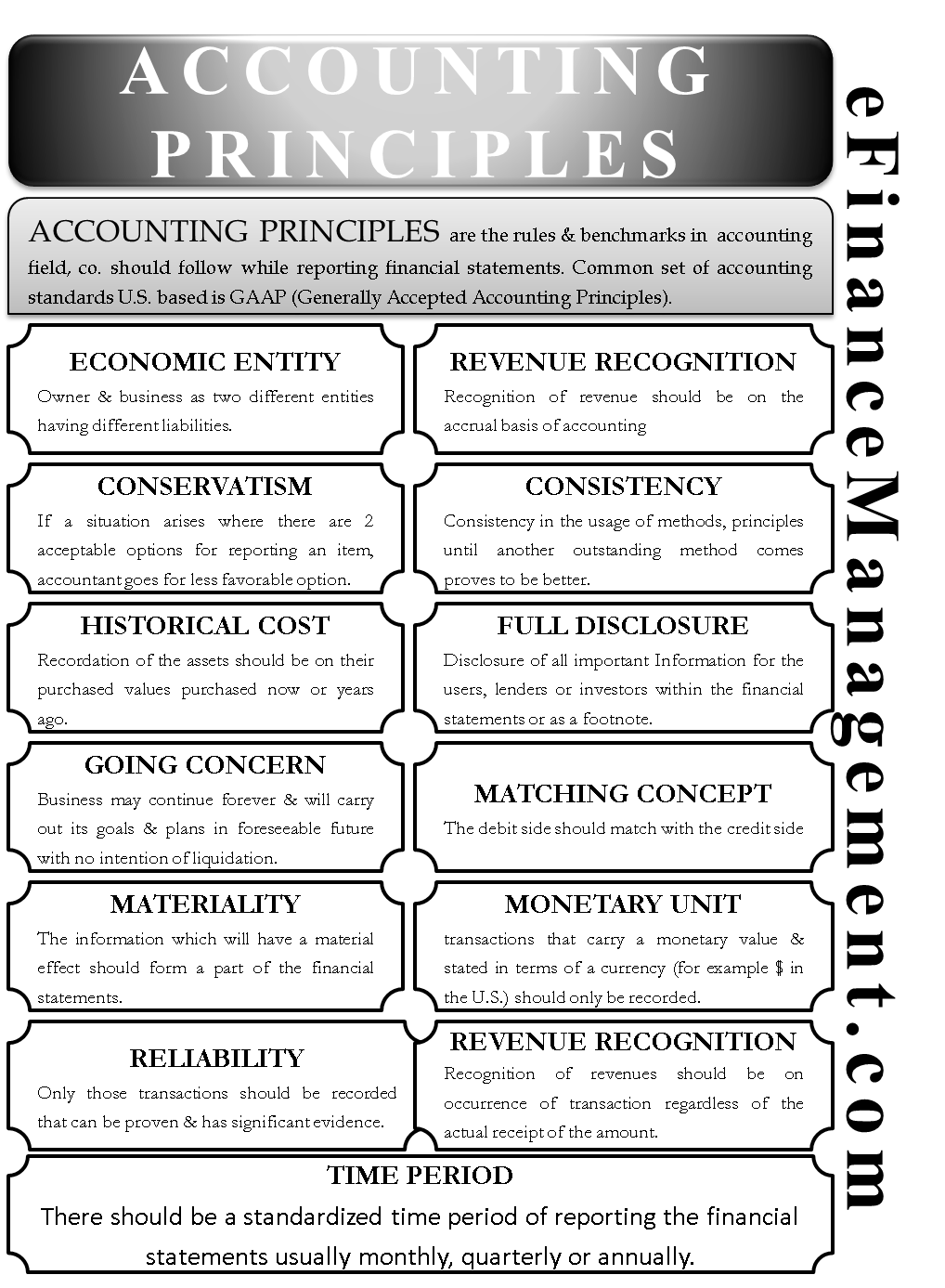
What are the five major GAAP principles?
The role of the Auditor is to examine and provide assurance that financial statements are reasonably stated under the rules of appropriate accounting principles. The auditor conducts the audit under a set of standards known as Generally Accepted Auditing Standards. The accounting department of a company and its auditors are employees of two different companies.
The economic entity principle distinguishes between personal and business finances. It treats the firm as a separate accounting entity, limiting the mixing of personal and corporate assets and liabilities and improving financial transparency. Therefore, the going concern concept by assuming that the business will not liquidate in the foreseeable future states that the firm should record the machinery’s value for its estimated life span. Now, the firm may charge ₹10,000 for 10 years from the profit and loss account. The international financial reporting standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), is an alternative to GAAP that is widely used worldwide. All negative and positive values on a financial statement, regardless of how they reflect upon the company, must be clearly reported by the accounting team.
Businesses should record any financial transactions that could materially affect business decisions. Even if this results in minor transactions being recorded, the idea is that it’s better to give a comprehensive look at the business — this is especially important in the event of an audit. Cost Benefit Principle – limits the required amount of research and time to record or report financial information if the cost outweighs the benefit. Thus, if recording an immaterial event would cost the company a material amount of money, it should be forgone. As a business language, accounting must be simple to understand for the people who own or manage the company’s affairs. So, to achieve that purpose, standards were invented that were uniform, scientific, and easily adaptable for all.
Equity capital specifies the money paid into a business by investors in exchange for stock in the company. Debt capital covers money obtained through credit instruments such as loans. Beyond basic accounting terms, this resource also explains alternative word uses and defines related or adjacent concepts. Importantly, it also covers relevant etymologies and word histories in cases where knowledge of these elements can help you better understand the term.
Dividends paid to shareholders also have a normal balance that is a debit entry. Since liabilities, equity (such as common stock), and revenues increase with a credit, their “normal” balance is a credit. Table 3.1 shows the normal balances and increases for each account type. The basic components of even the simplest accounting system are accounts and a general ledger. An account is a record showing increases and decreases to assets, liabilities, and equity—the basic components found in the accounting equation. As you know from Introduction to Financial Statements, each of these categories, in turn, includes many individual accounts, all of which a company maintains in its general ledger.
For example, the $120,000 cost of equipment with a 10-year life will be charged to expense at a rate of $1,000 per month. It also means that financial statements can be prepared for a group of separate legal corporations that are controlled by one corporation. This group of commonly owned corporations is referred to as the economic entity. The set of financial statements that reports the combined activity of the group is referred to as consolidated financial statements. Some of the accounting principles in the Accounting Research Bulletins remain in effect today and are included in the Accounting Standards Codification.
Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.